5.3.9. JNDI¶
5.3.9.1. Introduction¶
JNDI (Java Naming and Directory Interface, Java Naming and Directory Interface) is an API that provides naming and directory access services for Java applications, allowing clients to discover and look up data and objects by name, and is used to provide configuration-based dynamic calls. These objects can be stored in different naming or directory services such as RMI, CORBA, LDAP, DNS, etc.
The Naming Service is similar to the K/V pair of the hash table, and the corresponding service is obtained by name. Directory Service is a special Naming Service that uses a directory-like way to access services.
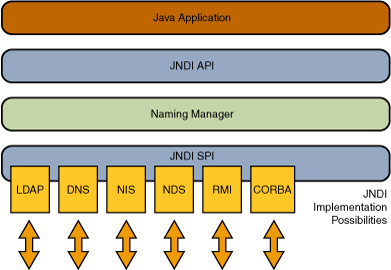
5.3.9.2. JNDI injection¶
JNDI injection was proposed by pentester about A Journey From JNDI LDAP Manipulation To RCE in the Blackhat USA on 2016.
The attack process is as follows:
Attacker binds payload to attacker’s naming/directory service/目录服务中
Attacker injects absolute URL into vulnerable JNDI lookup method
Application performs lookup
The application connects to the attacker-controlled JNDI service and returns a payload
The application decodes the response and triggers the payload
5.3.9.3. Attack payload¶
JDNI mainly has several attack payloads:
CORBA
IOR
JNDI Reference
LDAP
Remote Location
Remote Object
RMI
Serialized Object
5.3.9.3.1. RMI Remote Object¶
The attacker implements an RMI malicious remote object and binds it to the RMI Registry, and puts the compiled RMI remote object class on a server such as HTTP/FTP/SMB. The Codebase address is set by the remote server’s java.rmi.server.codebase property for remote loading by the victim’s RMI client.
The conditions of use are as follows:
The context of the RMI client allows access to the remote Codebase.
java.rmi.server.useCodebaseOnlyThe value of property is false.
After JDK 6u45、7u21,java.rmi.server.useCodebaseOnly the default value is true.
5.3.9.3.2. RMI + JNDI Reference¶
The attacker returns a JNDI Naming Reference through the RMI service. When the victim decodes the Reference, it loads the Factory class at the remote address specified by the attacker. In principle, this method does not use the RMI Class Loading mechanism, so it is not restricted by java.rmi.server.useCodebaseOnly system properties. But after JDK 6u132, JDK 7u122, JDK 8u113, the feature of JNDI Reference remote loading Object Factory class in Naming/Directory service is restricted. The default value of the system property com.sun.jndi.rmi.object.trustURLCodebase, becomes false, that is, the reference factory class is not allowed to be loaded from the remote Codebase by default .com.sun.jndi.rmi.object.trustURLCodebase .
5.3.9.3.3. LDAP + JNDI Reference¶
Java’s LDAP can store specific Java objects in attribute values, and the reference remote loading Factory class of LDAP services is not limited by com.sun.jndi.rmi.object.trustURLCodebase` attributes com.sun.jndi.cosnaming.object.trustURLCodebase such as , and has a wider scope of application.